Introduction
Python is one of the most popular programming languages today. If you are starting your coding journey, the first thing you need to understand is variables. Variables are the building blocks of any program. But what exactly is a variable in Python? How do they work, and why are they so important? In this guide, we’ll explain everything you need to know about variables in Python, step by step, with clear examples and practical tips.
By the end of this article, you will not only understand what a variable in Python is but also how to use it effectively in your programs. Whether you are a student, a beginner programmer, or someone curious about coding, this article will help you build a strong foundation.
What is a Variable in Python?
A variable in Python is like a storage box. It holds information that your program can use later. Think of it as a label on a container. You can put numbers, text, or even more complex data inside it. Later, you can open the container using the label and use what’s inside.
For example, if you have a variable named age and store 25 in it, your program now knows that age equals 25. Variables make your code flexible. You don’t need to hard-code values again and again. Instead, you store them in variables and use them wherever needed.
Why Variables Are Important in Python
Variables are essential for several reasons. First, they help you store data in memory. Second, they make your code readable and easy to maintain. Without variables, every number or word would need to be written directly in the code, which can be confusing.
Imagine building a game. You need to store player scores, names, and levels. Variables allow you to do this efficiently. They also make your code dynamic. If a value changes, you only need to update the variable, and the program will automatically use the new value.
How to Create a Variable in Python
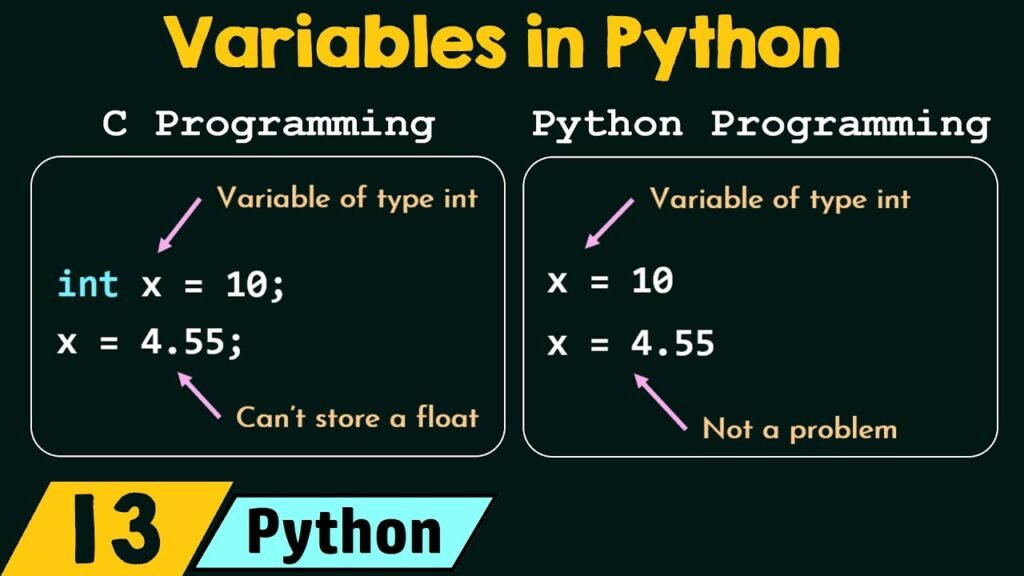
Creating a variable in Python is simple. You just need a name and a value. Python does not require you to declare the type of the variable, unlike other programming languages.
Example:
name = "Ravali"
age = 25
Here, name is a variable holding the text "Ravali", and age is a variable holding the number 25. Python automatically understands the type of variable based on the value you assign.
Rules for Naming Variables
Variable names in Python must follow some rules.
- Names can only contain letters, numbers, and underscores.
- They cannot start with a number.
- Python keywords like
for,if, orwhilecannot be used as variable names. - Names are case-sensitive (
ageandAgeare different).
Following these rules ensures your code works correctly and avoids errors.
Types of Variables in Python
Python supports different types of variables. Some common ones are:
- Integer: Whole numbers like
10,25, or100. - Float: Decimal numbers like
10.5,3.14. - String: Text like
"Hello"or"Python". - Boolean: True or False values.
Understanding variable types is important because certain operations work differently depending on the type.
Changing the Value of a Variable
One of the advantages of variables is that their values can change. For example:
score = 10
score = 15
Here, the variable score initially held 10. Later, it was updated to 15. Python automatically replaces the old value with the new one. This makes your code flexible and dynamic.
Variable Scope in Python
A variable’s scope determines where it can be used in your program. There are mainly two types:
- Local Variables: Defined inside a function and accessible only there.
- Global Variables: Defined outside functions and accessible everywhere.
Example:
x = 10 # Global variable
def my_function():
y = 5 # Local variable
print(y)
print(x) # Works
Understanding scope is crucial to avoid errors and unexpected behavior.
Constants vs Variables
Sometimes, you want a value to remain unchanged. These are called constants. Python does not have a built-in constant type, but by convention, variables in all capital letters are treated as constants.
Example:
PI = 3.14159 # Constant
Unlike constants, regular variables can change values anytime in the program.
Best Practices for Using Variables
- Use meaningful names:
ageis better thana. - Keep names lowercase, separate words with underscores:
user_name. - Avoid single letters except for counters:
i,j. - Update variables carefully to prevent bugs.
Following best practices makes your code readable and professional.
Real-Life Example of Variables
Imagine you are creating a simple shopping app. You can use variables to store items, prices, and total cost:
item_name = "Laptop"
price = 750
quantity = 2
total_cost = price * quantity
print(total_cost)
Here, variables make it easy to calculate costs and update prices dynamically.
Common Mistakes Beginners Make
- Using Python keywords as variable names.
- Forgetting the difference between local and global variables.
- Using inconsistent naming conventions.
- Assuming variables can hold multiple types simultaneously without proper handling.
Avoiding these mistakes will save time and frustration.
Advanced Tips for Variables
- Python allows multiple assignments in one line:
a, b, c = 1, 2, 3
- You can swap variables easily:
a, b = b, a
- Python variables are references, meaning multiple variables can point to the same data. Understanding this helps in optimizing memory usage.
FAQs About Variables in Python
1. Can a variable name start with a number?
No. Variable names cannot start with numbers. They must start with a letter or an underscore.
2. Are Python variables typed?
Python is dynamically typed, which means you don’t need to declare the type. Python infers it automatically.
3. Can a variable hold multiple values?
Yes, using data structures like lists, tuples, or dictionaries.
4. What happens if I use a variable before defining it?
Python will give an error called NameError. Always define a variable first.
5. Can variable names contain spaces?
No. Use underscores instead of spaces, like user_name.
6. What is the difference between global and local variables?
Global variables are accessible anywhere in the program, while local variables exist only inside a function.
Conclusion
Variables are the heart of Python programming. They allow you to store, update, and manage data effectively. By understanding what a variable in Python is, following naming rules, and using best practices, you can write clean and efficient code.
Start experimenting with variables today. what is variable in python Try creating your own programs and see how changing variable values can make your code dynamic. Python is powerful, and mastering variables is your first step toward becoming a skilled programmer.